Définition de la réalité virtuelle
La réalité virtuelle (ou Virtual Reality en anglais) est une expression qui désigne les dispositifs permettant de simuler numériquement un environnement par la machine (ordinateur). Selon les technologies employées, elle permet à l’utilisateur de ressentir un univers virtuel par le biais de ses différent sens : la vue le plus souvent mais aussi le toucher, l’ouïe, l’odorat.
La réalité virtuelle permet donc à une personne de vivre une expérience d’immersion et de mener une activité senso-motrice dans un monde artificiel. Pour garantir une immersion totale, l’utilisateur se sert d’un casque de réalité virtuelle. Celui-ci utilise le principe d’affichage en 3D stéréoscopique pour placer le visualisateur dans un monde virtuel généré par une machine.
La réalité virtuelle: une histoire pas si récente
Quand on parle de réalité virtuelle aujourd’hui, on pense immédiatement aux casques VR qui se démocratisent de plus en plus dans un large panel de secteur : jeux vidéo, immobilier, industrie, évènementiel… Comme nous l’avons vu, la réalité virtuelle comprend en réalité toutes les technologies plongeant un utilisateur dans un environnement artificiel, et ce quel que soit le sens impliqué.

La première machine de réalité virtuelle est attribuée à Morton Hellig et sa machine « Sensorama ». Ce dispositif datant de 1956 permet à l’utilisateur de ressentir des effets faisant appel à plusieurs sens (toucher, odorat, ouïe…). Plusieurs dispositifs similaires verront le jour par la suite mais resteront purement expérimentaux.
Il faudra attendre le début des années 90’ pour entrevoir l’apparition des premiers casques de réalité virtuelle tel qu’on les connaît de nos jours. C’est d’abord la NASA qui donne la première impulsion dans la réalisation de casque VR grâce à des programmes de recherche qui permettront une multitude de progrès dans ce domaine. L’interaction se faisait alors grâce à un système haptique (par le toucher).
Plusieurs casques « grand public » suivront, notamment dans le domaine des jeux vidéos mais seront principalement des échecs commerciaux. Leurs prix prohibitifs, la faible qualité délivrée ainsi que leur inconfort auront raison de cette génération de casques. Le public n’est pas au rendez-vous et le casque réellement immersif reste encore un fantasme.
Occulus Rift : une révolution technologique de la VR

Dès l’année 2009, un jeune américain mordu d’électronique, Palmer Luckey, se lance dans un projet de casque de réalité virtuelle dont il va sortir plusieurs prototypes. En partageant ses avancements sur internet, il fait la rencontre de John Carmack, le président d’id Software, studio à l’origine de grands titres du jeu vidéo. Celui-ci va permettre d’étendre largement la notoriété de ce projet et d’attirer certains grands noms du secteur. Palmer lance par la même occasion un projet de financement Kickstarter dont l’objectif est remplit en moins de 24h.
Suite au succès de cette campagne, Palmer Luckey décide alors de créer sa propre structure nommée Oculus VR qui conduira à la commercialisation du célèbre casque VR que l’on connait actuellement : L’Occulus Rift. Il vendra par la suite cette société à Facebook pour plusieurs milliards de dollars.
Téléchargez notre dernière infographie et découvrez toutes les solutions de réalité immersive !
La réalité virtuelle: un outil professionnel
La réalité virtuelle et plus précisément les casques VR se sont développés dans un premier temps dans l’objectif d’améliorer profondément l’expérience vidéo ludique par une immersion totale à 360°. La technologie faisait directement suite au rendez-vous manqué dans les années 90 et promettait de devenir un incontournable du divertissement. Les principaux verrous technologiques avaient sauté.
Mais le prix des casques et du matériel, les freins techniques (espace nécessaire, mouvements réduits) et l’offre de jeux limitée ont finalement trouvé d’autres voies de développement. C’est dorénavant le monde professionnel qui adopte ces casques immersifs. La maturité de cette technologie croisée à l’avènement du marketing expérientiel a donc propulsé la VR à travers différents secteurs professionnels sur lesquels nous allons nous pencher.
La réalité virtuelle dans l’immobilier
La réalité virtuelle dans l’immobilier s’est peu à peu démocratisée, notamment par le biais de la visite virtuelle immersive et non-immersive. Celle-ci donne la possibilité de s’immerger dans un projet immobilier, améliorant alors grandement la capacité de projection des clients.
Les Visites à 360°, les interactions et le réalisme bluffant de la 3D viennent séduire de plus en plus de professionnels de l’immobilier. Il existe deux types d’outils :
Les visites immersives immobilières
Soyons clairs, les outils utilisant les casques VR dans l’immobilier restent pour l’instant réservés à certains projets haut- de-gamme, mis en avant, notamment en bulles de vente. Que ce soit des visites de bureaux, ou de résidences luxueuses, c’est généralement un dispositif de haute qualité qui vient compléter une application. Modélisations 3D, films virtuels, captures à 360° et création d’interfaces, c’est outil à part entière qui viendra sublimer et scénariser les visites. De plus, l’immersion est une véritable expérience, souvent inconnue qui est vécue par le visualisateur. Il en ressort bluffé, immergé et donc rassuré sur son intention d’achat.
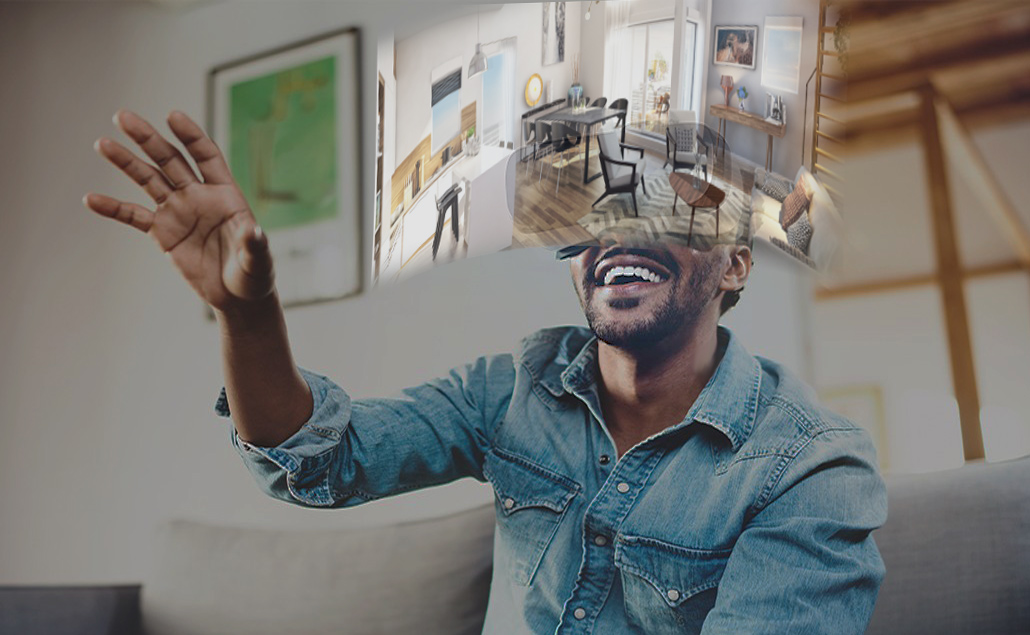

Les visites virtuelles immobilières
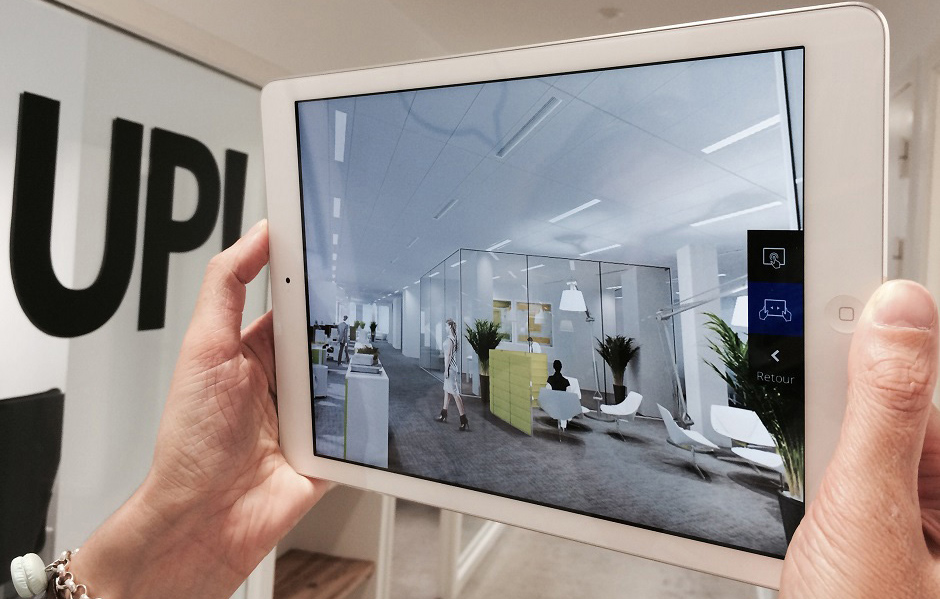
Les visites virtuelles “non-immersives” ne sont pas non plus en reste. Maquettes 3D, 360° tactile et applications pour tablettes viennent s’ajouter aux outils des équipes commerciales. Ils permettent de comprendre, visiter et interagir avec un projet immobilier avant et pendant construction. Il complète la vente sur plan et permet aux clients de réellement voir ce qu’ils envisagent d’acheter dans son contexte (espaces verts, commerces à proximité, transports).
Ces outils cumulent plusieurs technologies en une seule application. Ils peuvent également être intégrés sur un site web afin de laisser les visiteurs découvrir et s’informer d’eux-mêmes sur le projet.

la réalité virtuelle dans l’industrie
L’industrie s’est également emparée de la réalité virtuelle. Visite de chaîne de production, d’usine ou maquette d’une future construction d’usine.
Les visites virtuelles immersives industrielles
Grâce à la VR, il est désormais possible de visiter une chaîne de production et transporter ses partenaires et/ou clients dans une usine.
À présent, les normes de sécurité ou d’hygiène n’empêchent plus la visite physique. Plus rare, certaines entreprises utilisent la VR à des fins de transparence vis-à-vis du consommateur. On l’a vu avec l’actualité, les scandales sanitaires et l’opacité des process de transformation ont entachés la réputation de plusieurs sociétés.
Certaines d’entre-elles ont donc joué sur la transparence en utilisant cette technologie de visite virtuelle et proposent dorénavant ce système. Ne nécessitant pas ou peu d’interactivité, ces solutions sont majoritairement disponibles sur des casques dit “nomades” comme le Samsung Gear VR, ou encore l’Oculus GO.
La formation par la réalité virtuelle
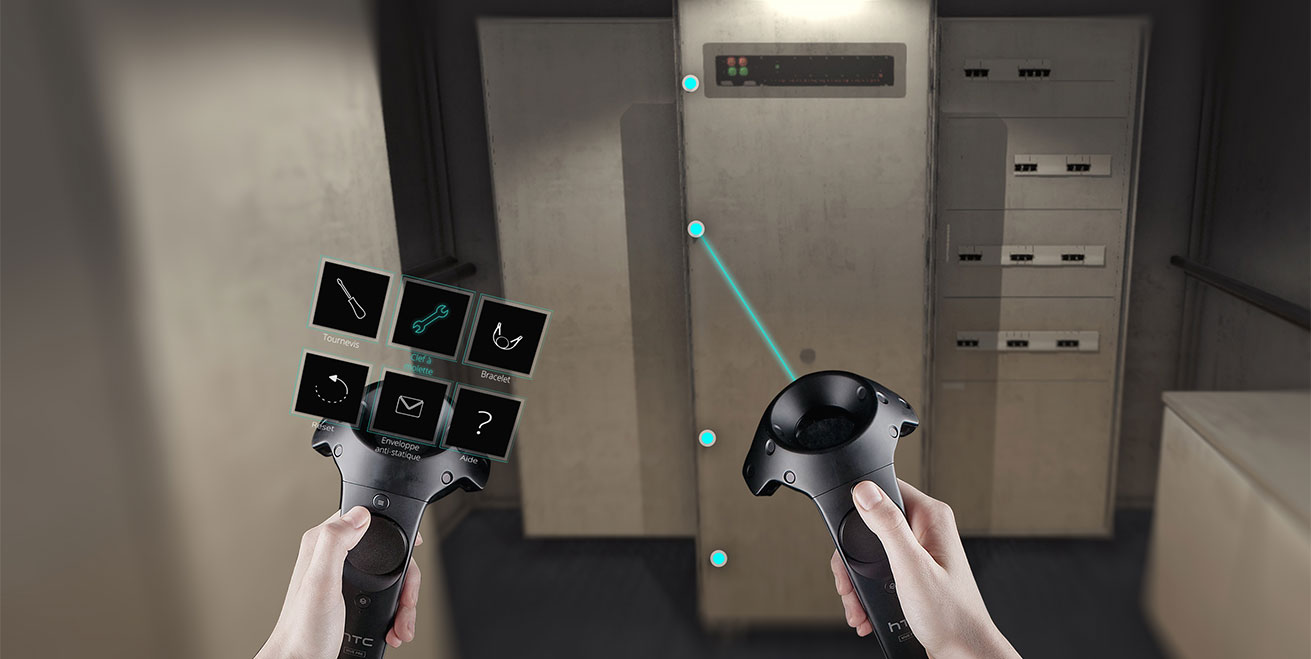
Autres usages dans l’industrie, les outils d’aide à la formation ou à la maintenance se multiplient. Ils permettent d’intégrer des process industriels dans un outil de réalité virtuelle et de les inculquer à la personne formée avant d’intervenir sur site. Manipulation, tutoriels scénarisés, les casques VR permettent de réaliser de véritables expériences immersives et interactives. L’intégralité du poste de travail est modélisé dans une 3D réaliste et immerge l’apprenant. De plus, des situations impossibles à simuler dans le réel peuvent être intégrer à la scénarisation : incidents, anomalies, risques, etc..
Côté matériel, les formations se font quasi exclusivement sur les casques VR dit “sédentaires” comme le HTC Vive ou l’Oculus Rift. Disponibles avec des manettes de contrôle, ils permettent d’interagir directement sur l’environnement virtuel de manière fidèle au réel. Le fait de pouvoir répéter autant que voulu la formation en VR est également un gain non négligeable dans la phase d’apprentissage.

Les visites virtuelles industrielles
Tout comme dans l’immobilier, les usines se visitent également grâce à des outils de visites virtuelles. Grâce à une maquette 3D interactive, il est maintenant possible de visualiser l’intégralité des bâtiments avant qu’ils ne soient construits, ou encore sans devoir se déplacer. C’est l’outil idéal pour une présentation réaliste et pratique auprès des collaborateurs et investisseurs grâce à des fonctionnalités, telles que l’ajout de vues à 360° sous forme de points d’intérêts ou l’intégration de la décomposition par couche, de la technicité ou encore de la gestion des flux.

La VR s’installe dans les musées
Musées, châteaux et lieux d’intérêts culturels, beaucoup se mettent à utiliser la réalité virtuelle immersive afin de proposer d’autres manières de visiter ou de faire découvrir des lieux inaccessibles. Proposées principalement sous forme d’application, celles-ci ont l’avantage d’intégrer des contenus scénarisés : films, points d’intérêts, reconstitutions en 3D, etc. Ces visites virtuelles donnent un second degré de compréhension aux visiteurs en y apportant des éléments supplémentaires. Elles peuvent également être une véritable attraction pour les enfants dans le cas d’un jeu, ou d’un contenu ludique par exemple.

La réalité virtuelle dans l’évènementiel
Autre secteur impacté par la VR : l’évènementiel. En effet, il est apparu évident pour de nombreuses marques qu’il fallait s’emparer de la réalité virtuelle pour promouvoir un évènement. De plus en plus de présentations de produits et de services se font par le biais de la réalité virtuelle. Cela permet par exemple de présenter un produit qui n’est pas obligatoirement présent sur place et laisse une plus grande marge créative pour la mise en scène. Il s’agit d’une véritable plus-value qui marque les esprits en proposant une expérience inédite.
La retransmission d’évènement en direct est également touché par la VR:
- Dans le domaine sportif, il est maintenant possible de voir en direct certains matchs à 360° de chez soi.
- Certains salons proposent des points de vues à 360°.
- Il est également possible de suivre certains spectacles en direct.
- Portes-ouvertes évenementielles
Ce nouveau type de divertissement est désormais réalité grâce au développement de dispositifs de capture à 360°. Ceux-ci sont placées stratégiquement pour offrir le meilleur panorama possible au spectateur et lui faire vivre l’événement de l’intérieur, comme si il y était, et ce depuis son salon, son bureau.
Dans ce contexte, la chaîne Fox propose par exemple l’accès à une suite virtuelle entièrement en 3D donnant des points de vue uniques sur les matchs.

S’immerger à 360° : quels-sont les casques VR sur le marché?
Depuis l’apparition de l’Occulus, de nombreux casques VR ont fait leur entrée. Nous allons ici les passer en revue et donner des détails sur leur gamme, leur technologie embarquée et leurs usages :

L’Occulus Rift : premier casque VR « nouvelle génération » et grand public. C’est un casque filaire connecté sur ordinateur proposant une bonne qualité d’affichage. Des manettes sont également disponibles afin d’interagir avec l’environnement virtuel diffusé dans le casque. Il nécessite l’installation de plusieurs capteurs afin de tracker le porteur du casque dans une pièce.

Le HTC Vive : concurrent direct de l’Occulus, le HTC vive est également un casque filaire (bientôt disponible en non-filaire) connecté sur PC. Il possède également des manettes et nécessite l’installation de deux capteurs afin de tracker l’utilisateur dans l’espace. Son champ d’action est cependant plus grand que celui de l’Occulus mais le HTC nécessite une configuration légèrement plus puissante que son rival.

Le Samsung Gear VR: autonome et connecté au smartphone Samsung, il est bien évidemment moins puissant que les deux modèles présentés ci-dessus. Il est cependant bien moins encombrant et délivre malgré tout une bonne expérience immersive. Il propose également d’interagir par le biais de petites manettes.

L’Oculus GO : Dernier né de chez Oculus, ce casque se positionne sur le même segment que le Samsung Gear VR. Contrairement à son homologue coréen, l’Oculus GO ne nécessite pas de smartphone pour fonctionner. L’objectif de la marque est de proposer un casque entièrement autonome à un tarif très abordable. Une télécommande trackée par le casque est également disponible afin de naviguer facilement dans les menus.
Le Google Cardboard: il s’agit du casque le moins coûteux du marché (seulement quelques euros) puisqu’il est fait en carton et est à plier soi-même. Il offre un premier aperçu de ce qu’est la VR et s’utilise en glissant son smartphone directement dans le casque. Il est parfait pour la lecture de simple 360°. il faut le maintenir soi-même sur sa tête.

Le Playstation VR: Uniquement disponible sur la console de jeu Playstation, il est avant tout dédié à certains jeux-vidéos disponibles sur le store dédié.
On l’aura remarqué, l’offre est vaste et propose des solutions particulièrement différentes, pour autant de finalités applicatives.
Conclusion
Les professionnels se sont donc emparés de ces technologies et de véritables outils performants en émergent. Immobilier, industrie, muséographie et événementiel, nous sommes à l’aube d’une modification profonde des usages des casques VR. De nouvelles applications voient le jour petit à petit, utilisant le meilleur de chaque technologie.
Chaque année qui passe voit apparaître de nouveaux usages pour la réalité virtuelle. La réalisation sur-mesure de ces outils permet de sans-cesse repousser les limites technologiques et créatives. L’usager est donc le principal moteur pour nos équipes afin de toujours délivrer des outils innovants et pertinents.
Deuxième cheval de bataille technologique, la réalité virtuelle est souvent mise en concurrence avec la la réalité augmentée ,notamment par les géants de la Silicon Valley.


